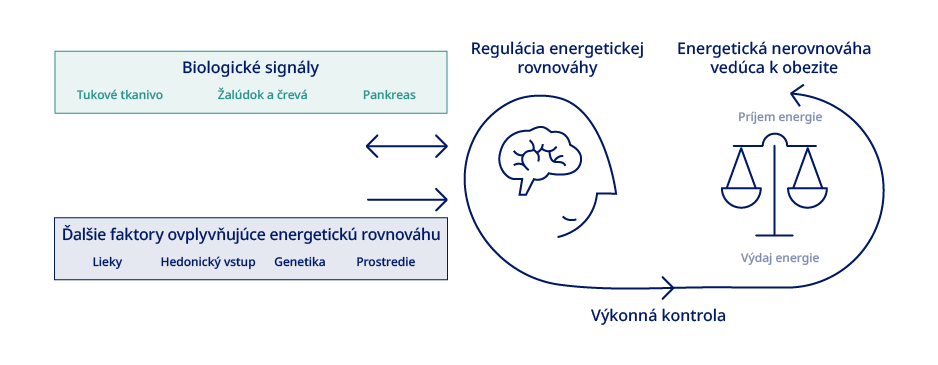
Pochopenie energetickej rovnováhy je kľúčové na pochopenie vedeckých poznatkov o obezite.3 Zmenená energetická rovnováha prispieva k patofyziológii obezity.3 U jedincov bez problémov s malabsorpciou sa uložená energia v tele zvyšuje len vtedy, ak celkový príjem energie (z konzumácie potravín/nápojov) prevyšuje celkový výdaj energie.3
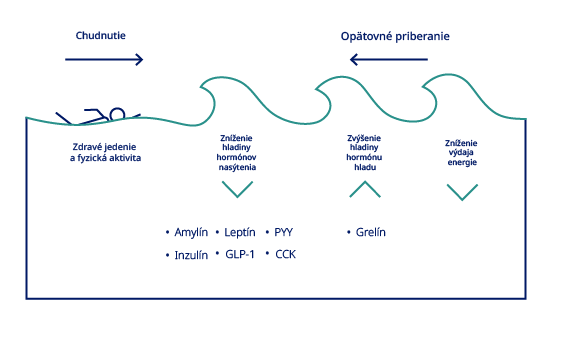
Výdaj energie môže prebiehať prostredníctvom fyzickej aktivity, bazálneho metabolizmu a adaptívnej termogenézy.3 Telo má komplexné homeostatické mechanizmy, ktorými sa snaží odolávať úbytku alebo prírastku hmotnosti.3 Príliš zjednodušené názory spočiatku hovorili, že obezita je dôsledkom dostupnosti potravy a vedomého konania.3 Na energetickej nerovnováhe sa však podieľa viacero molekulárnych dráh, ktoré prispievajú k obezite. Patrí k nim vplyv centrálneho nervového systému na správanie (napr. jedenie a fyzickú aktivitu) a tiež pôsobenie neuroendokrinného systému, ktorý kontroluje vylučovanie hormónov, ako sú leptín, inzulín, estrogén, rastové hormóny a hormóny štítnej žľazy.3
1. Sanyaolu A, Okorie C, Qi X, Locke J, Rehman S. Childhood and Adolescent Obesity in the United States: A Public Health Concern. Glob Pediatr Health. 2019;6:2333794X19891305.
2. Gadde KM, Martin CK, Berthoud HR, Heymsfield SB. Obesity: Pathophysiology and Management. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2018;71(1):69-84.
3. Spiegelman BM, Flier JS. Obesity and the regulation of energy balance. Cell. 2001;104(4):531-43.
4. Schwartz A, Doucet E. Relative changes in resting energy expenditure during weight loss: a systematic review. Obes Rev. 2010;11(7):531-47.
5. Sumithran P, Proietto J. The defence of body weight: a physiological basis for weight regain after weight loss. Clin Sci (Lond). 2013;124(4):231-41.
6. Rosenbaum M, Leibel RL. Adaptive thermogenesis in humans. Int J Obes (Lond). 2010;34 Suppl 1:S47-55.
7. Rosenbaum M, Kissileff HR, Mayer LE, Hirsch J, Leibel RL. Energy intake in weight-reduced humans. Brain Res. 2010;1350:95-102.
8. Greenway FL. Physiological adaptations to weight loss and factors favouring weight regain. Int J Obes (Lond) . 2015;39(8):1188-96.
9. Lenard NR, Berthoud HR. Central and peripheral regulation of food intake and physical activity: pathways and genes. Obesity (Silver Spring). 2008;16 Suppl 3:S11-22.
10. Sumithran P, Prendergast LA, Delbridge E, Purcell K, Shulkes A, Kriketos A, et al. Long-term persistence of hormonal adaptations to weight loss. N Engl J Med. 2011;365(17):1597-604.
11. Heymsfield SB, Wadden TA. Mechanisms, Pathophysiology, and Management of Obesity. N Engl J Med. 2017;376(15):1492.
12. Naef L, Pitman KA, Borgland SL. Mesolimbic dopamine and its neuromodulators in obesity and binge eating. CNS Spectr. 2015;20(6):574-83.
13. Liu CM, Kanoski SE. Homeostatic and non-homeostatic controls of feeding behavior: Distinct vs. common neural systems. Physiol Behav. 2018;193(Pt B):223-31.
14. Massicotte E, Deschenes SM, Jackson PL. Food craving predicts the consumption of highly palatable food but not bland food. Eat Weight Disord. 2019;24(4):693-704.
15. Yau YH, Potenza MN. Stress and eating behaviors. Minerva Endocrinol. 2013;38(3):255-67.
16. Lizcano F, Guzman G. Estrogen Deficiency and the Origin of Obesity during Menopause. Biomed Res Int. 2014;2014:757461.
17. Scacchi M, Pincelli AI, Cavagnini F. Growth hormone in obesity. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord. 1999;23(3):260-71.
18. Bandurska-Stankiewicz E. Thyroid hormones – obesity and metabolic syndrome. Thyroid Research. 2013;6.
19. Kanoski SE, Hayes MR, Skibicka KP. GLP-1 and weight loss: unraveling the diverse neural circuitry. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2016;310(10):R885-95.
20. Gonzalez Jimenez E. Obesity: etiologic and pathophysiological analysis. Endocrinol Nutr. 2013;60(1):17-24.
21. Zhao Y, Chen LB, Mao SS, Min HX, Cao J. Leptin resistance was involved in susceptibility to overweight in the striped hamster re-fed with high fat diet. Sci Rep. 2018;8(1):920
22. Petersen MC, Shulman GI. Mechanisms of Insulin Action and Insulin Resistance. Physiol Rev. 2018;98(4):2133-223.
23. Kim J, Lee J. Role of obesity-induced inflammation in the development of insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes: history of the research and remaining questions. Ann Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 2021;26(1):1-13.
24. Olarescu NC, Gunawardane K, Hansen TK, Moller N, Jorgensen JOL. Normal Physiology of Growth Hormone in Adults. In: Feingold KR, Anawalt B, Boyce A, Chrousos G, de Herder WW, Dhatariya K, et al., editors. Endotext. South Dartmouth (MA). 2000.
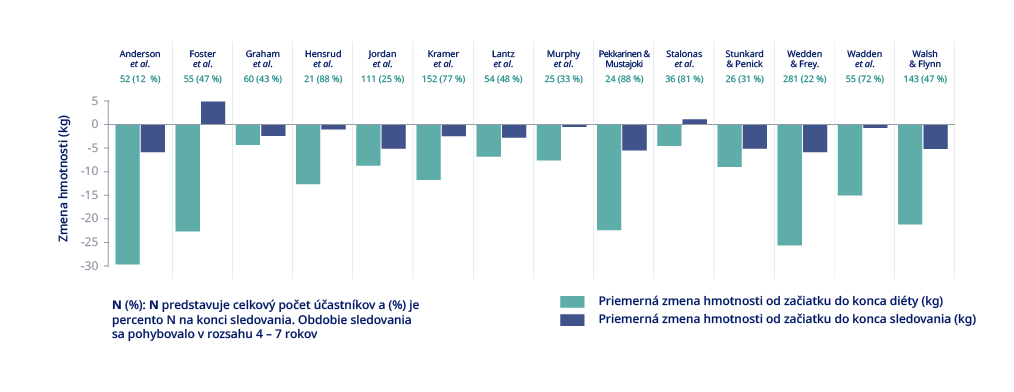
25. Mann T, Tomiyama AJ, Westling E, Lew AM, Samuels B, Chatman J. Medicare's search for effective obesity treatments: diets are not the answer. Am Psychol. 2007;62(3):220-33.
26. Caterson ID, Alfadda AA, Auerbach P, Coutinho W, Cuevas A, Dicker D, et al. Gaps to bridge: Misalignment between perception, reality and actions in obesity. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2019;21(8):1914-24.


.png)